External Trusted Secure Storage
Abstract
This document mainly introduces the motivation of adding External Trusted Secure Storage(ETSS) partition and the corresponding design proposal.
Introduction
A secure storage solution is very important when storage is external to MCU. Macronix and other Flash memory suppliers have developed several security memory products, and three major products are RPMC, Authentication Flash, and a more full featured secure Flash like Macronix ArmorFlash.
RPMC is a memory device which provides non-volatile monotonic counters for replay protection.
Authentication Flash mainly provides authentication mechanism to enhance the security of data transmition.
Compared to previous two security Flash, the full featured secure Flash performs authentication, encryption along with a full range of additional security features. This secure Flash generally equips with hardware crypto engine with advanced cryptography algorithms, physically unclonable function(PUF), non-volatile monotonic counters, TRNG, key storage and management module, etc. Secure Flash always provides protection against hardware attacks such as probing, side-attack and fault injection.
In addition, the communication channel between host MCU/SoC and secure Flash is protected by encryption, authentication, data scrambling, and frame sequencing with monotonic counters, as shown in Secure communication channel between host and secure Flash.Besides, the independent secure sections configured with specific security policy satisfies multi-tenant isolation.
Hence the secure Flash provides dependable defense against unauthorised access, man-in-the-middle, replay, sniffing and other security threats.
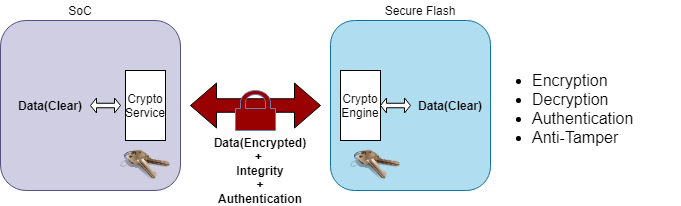
Figure 1: Secure communication channel between host and secure Flash
More information about secure Flash can be extracted from Macronix ArmorFlash product introduction 1 and the ArmorFlash Whitepaper 2 for understanding the secure memory architectures in emerging electronic systems.
Design concept
Overview
An ETSS partition is developed as a PSA RoT secure partition to provide external trusted secure storage services based on above external security memory products features. These three major security memory products are collectively referred to as secure Flash in the following. The ETSS partition includes several software components, which are listed below:
Component name
Description
service API
The service interface of ETSS partition to the NSPE/SPE
Service module
This module handles the service calls from NSPE/SPE
Secure Flash framework module
This module is the generic framework of secure Flash driver.
The interaction between these different components is illustrated in the following block diagram:
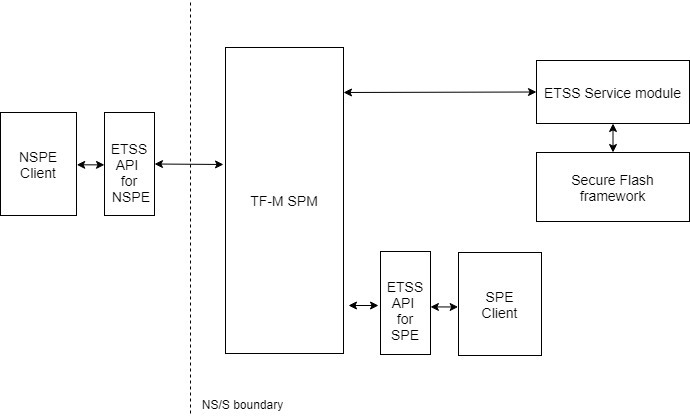
Figure 2: Block diagram of the different components of ETSS partition.
The more detailed architecture of ETSS service with secure Flash framework is shown below.
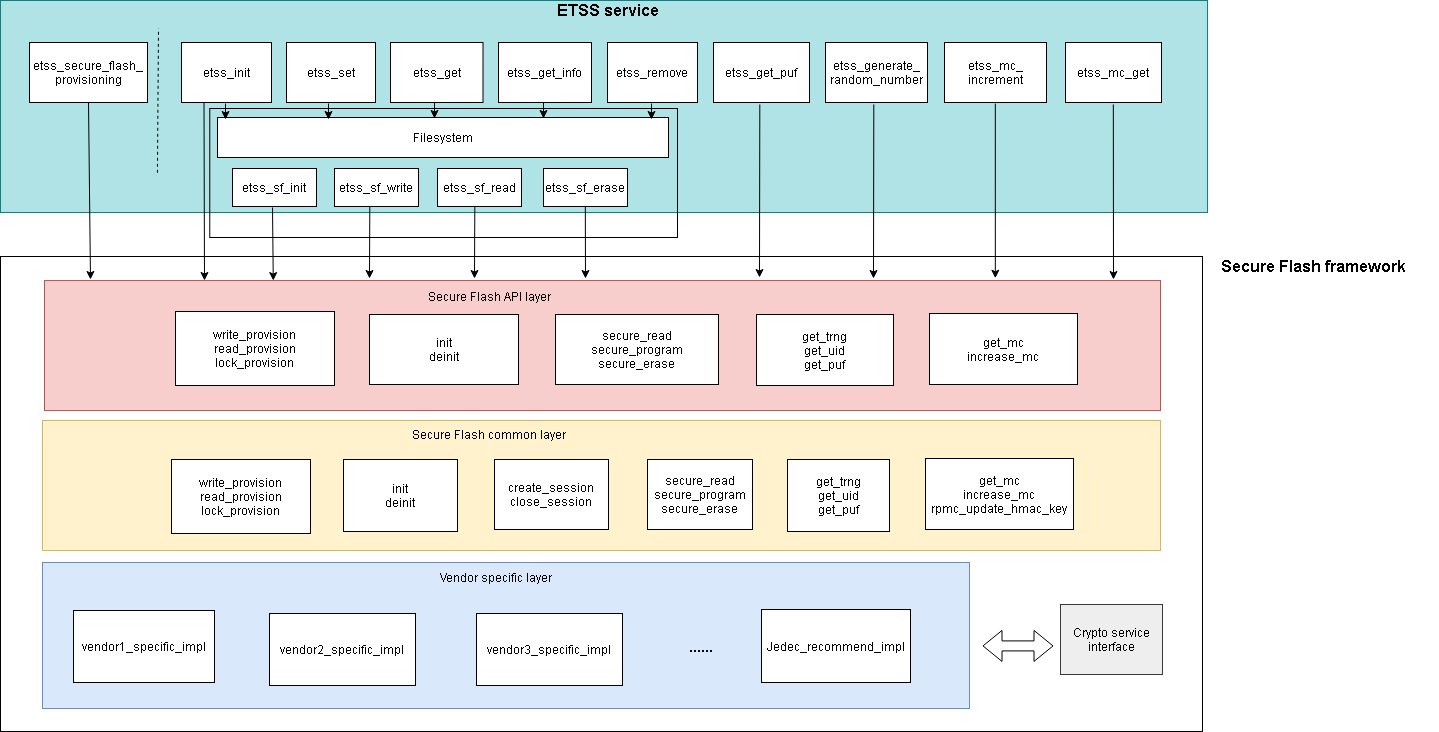
Figure 3: Layered architecture of ETSS service with secure Flash framework
ETSS services can be accessed by other services running in SPE, or by applications running in the NSPE.
ETSS services are split into two independent parts: provisioning and deployment.
A secure Flash provisioning process should be performed before deployment to set
up binding keys and grant access rights. The etss_secure_flash_provisioning
service is provided to perform secure Flash provisioning in the manufacture
process. The specific provisioning implementation may vary with security memory
vendors and platforms.
After provisioning, ETSS is ready for providing deployment services with external secure Flash. The available services vary with security memory products. There are three types of services:
Secure storage
Replay protection monotonic counter manipulation
Extra services based on extended security features(such as PUF, true random number generator, etc.)
The actually available services are based on the security features of backend secure Flash.
Taking following scenarios for example:
The external security memory product is just an RPMC, only monotonic counters manipulation services are available.
The external security memory product is a full featured secure Flash, it supports security read, security program, has a certain number of monotonic counters and other extra security functions. Then the holistic ETSS services may be available.
In the current implementation, ETSS partition just copies the concise filesystem implemented in TF-M ITS partition. As this filesystem doesn’t involve access rights management, to support secure Flash multi-zone isolation, it needs to declare separate filesystem contexts for each secure Flash isolated partition. The detailed layout of each isolated partition is set up by the specific secureflash_layout.h of each secure Flash. For each specific security memory products, the secureflash_layout.h should be configured according to the application scenario.
If user needs to support two and more security memory products simultaneously in ETSS partition, then corresponding secure Flash instances and filesystem contexts should be declared.
The secure Flash framework module aims to generalize the application interface of secure Flash driver, and cover different vendors’ security memory products. It can be intergated with different software platforms and OSes, and consists of four parts: secure Flash API layer, secure Flash common layer, vendor specific layer and crypto service interface.
Secure Flash API layer: This layer mainly manages application’s access permission based on application identification and pre-provisioned information. The implementation of this layer varies accross software platforms and OSes. Here integrated with TF-M, this layer manages access permissions based on client id, and derives parameters passed to secure Flash common layer.
Secure Flash common layer: This layer abstracts secure Flash operations, and calls binding vendor specific operations.
Vendor specific layer: The specific implementation of different secure Flash vendors and JEDEC recommended implementation, it depends on upper layer’s choice to bind with JEDEC recommended implementation or vendor specific implementation. This layer calls tf-m crypto services via crypto service interface to perform cryptographic operations, then assemble packets sent to external secure Flash and parse packets received from external secure Flash.
If vendors tend to contribute projects with hiding some critical source codes, then these critical parts can be released as library files. These library files may be maintained in another git repository because of different license, vendors should explain how to access these library files in relevant documents.
Code structure
The code structure of this partition is as follows:
tf-m-extras repo:
partitions/external_trusted_secure_storage/etss_partition/
etss.yaml- ETSS partition manifest fileetss_secure_api.c- ETSS API implementation for SPEetss_req_mngr.c- Uniform IPC request handlersexternal_trusted_secure_storage.h- ETSS API with client_id parameterexternal_trusted_secure_storage.c- ETSS implementation, using secureflash_fs as back-endsecureflash_fs/- Secure Flash filesystemexternal_secure_flash/- Secure Flash filesystem operationssecureflash/- Backend secure Flash framework for ETSS servicesecureflash.c- Secure Flash API layer interfaces implementationsecureflash.h- Secure Flash API layer interfacessecureflash_common/- Secure Flash common layer of secure Flash frameworkcrypto_interface/- Crypto service interface of secure Flash frameworkJEDEC_recommend_impl/- Reserved JEDEC recommend uniform implementationmacronix/- Macronix specific implementationsecureflash_vendor2/- Reserved vendor2 specific implementationsecureflash_vendor3/- Reserved vendor3 specific implementation
template/- Templates of underlying hardware platform specific implementation of ETSS service
interface/
include/etss/etss_api.h- ETSS APIinclude/etss/etss_defs.h- ETSS definitionssrc/etss/etss_ipc_api.c- ETSS API implementation for NSPE
suites/etss
non_secure/etss_ns_interface_testsuite.c- ETSS non-secure client interface test suitesecure/etss_s_interface_testsuite.c- ETSS secure client interface test suitesecure/etss_s_reliability_testsuite.c- ETSS secure interface reliability test suite
tf-binaries repo:
macronix/commonBinaryMX75/
mx75_armor_lib.a- The binary library of Macronix mx75 series ArmorFlash
Note
The suites/etss/ provides ETSS service test suites, this folder can be
integrated with tf-m-tests/test/suites for testing.
Configuration and Build
Currently, only GNUARM is supported to build as an out-of-tree Secure Partition.
To test etss service, put external_trusted_secure_storage/interface/include/etss
under trusted-firmware-m/interface/include, put external_trusted_secure_storage/interface/src/etss
under trusted-firmware-m/interface/src.
Add corresponding command within trusted-firmware-m/interface/CMakeLists.txt.
Besides, to integrate ETSS testsuites sample with tf-m-tests, put the
suites/etss folder under tf-m-test/test/suites, add following command to
tf-m-test/test/suites/CMakeLists.txt.
add_subdirectory(suites/etss)
and add the following command to ``tf-m-test/app/CMakeLists.txt``
$<$<BOOL:${TFM_PARTITION_EXTERNAL_TRUSTED_SECURE_STORAGE}>:${INTERFACE_SRC_DIR}/etss/etss_ipc_api.c>
build with the following commands.
cd <TF-M base folder>
cmake -S . -B cmake_build -DTFM_PLATFORM=stm/stm32l562e_dk \
-DTFM_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=toolchain_GNUARM.cmake -DTEST_S=ON -DTEST_NS=ON \
-DTFM_EXTRA_MANIFEST_LIST_FILES=<tf-m-extras-abs-path>/partitions/external_trusted_secure_storage/etss_manifest_list.yaml \
-DTFM_EXTRA_PARTITION_PATHS=<tf-m-extras-abs-path>/partitions/external_trusted_secure_storage/etss_partition \
-DTFM_PARTITION_EXTERNAL_TRUSTED_SECURE_STORAGE=ON -DTFM_ISOLATION_LEVEL=2
cmake --build cmake_build -- install
Note
<tf-m-extras-abs-path>:The absolute path of tf-m-extras folder. The corresponding trusted-firmware-m version is v1.4.0. At the moment, ETSS partition has been tested with STM32L562E_DK development board. As this development board hasn’t carried any secure Flash. An external secure Flash is connected to MCU by fly lines.
Future changes
Currently, the implementation of secure Flash provisioning service is primitive, and only suitable for developer mode. In the future, a proper secure Flash provisioning implementation will be provided.
- Besises, the following works are underway:
Optimize secure Flash sessions management.
Add access rights management features to secure Flash filesystem.
References
Copyright (c) 2021-2022, Macronix International Co. LTD. All rights reserved. SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause